- +91 98410 45284
- No.8A, Dr Nair Road, T.Nagar, Chennai-600017
- Consultation only by Appointments
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
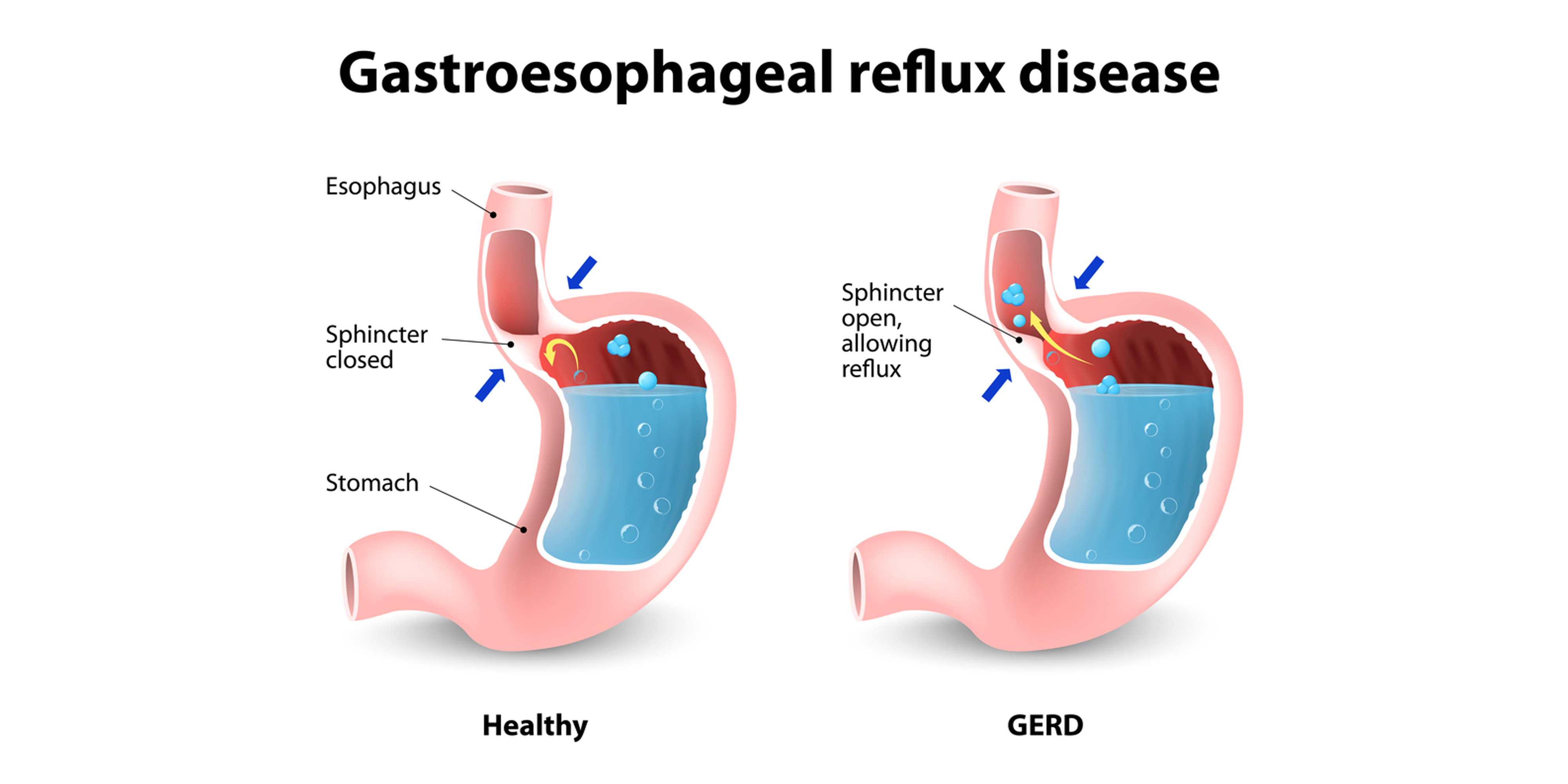
Gastroesophageal refers to the stomach and esophagus and reflux means back flow or return. So, gastroesophageal reflux is a disease in which the contents of stomach return back into the esophagus. It is a chronic digestive disease that can irritate the esophagus and cause heartburn and other symptoms.
When food is swallowed, the lower oesophageal sphincter muscle relaxes to allow food and liquid to flow down to stomach. Then LES closes. But if LES becomes weak or relaxes inappropriately, stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus, causing frequent heartburn. Other than this, there are some more contributing factors like:
⦿ Foods and beverages like chocolate, peppermint, fried or fatty foods, coffee, or alcoholic beverages may trigger reflux Cigarette smoking Obesity
⦿ Pregnancy
⦿ Hiatal hernia
⦿ Scleroderma
⦿ Certain medications like beta-blockers etc.
⦿ Foods and beverages like chocolate, peppermint, fried or fatty foods, coffee, or alcoholic beverages may trigger reflux Cigarette smoking Obesity
⦿ Pregnancy
⦿ Hiatal hernia
⦿ Scleroderma
⦿ Certain medications like beta-blockers etc.
Symptoms of GERD generally get worse on bending over or laying down, or on eat and at night.
⦿ Heartburn or a burning sensation in chest (heartburn)
⦿ The burning begins behind the breastbone and move upward to the neck and throat
⦿ Food coming back into the mouth causing an acid or bitter taste
⦿ Chest pain
⦿ Nausea after eating
⦿ Difficulty swallowing
⦿ Feeling of food stuck behind the breastbone
⦿ Dry cough or wheezing
⦿ Hoarseness or sore throat
⦿ Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
⦿ Sensation of a lump in throat
⦿ Hiccups
⦿ Heartburn or a burning sensation in chest (heartburn)
⦿ The burning begins behind the breastbone and move upward to the neck and throat
⦿ Food coming back into the mouth causing an acid or bitter taste
⦿ Chest pain
⦿ Nausea after eating
⦿ Difficulty swallowing
⦿ Feeling of food stuck behind the breastbone
⦿ Dry cough or wheezing
⦿ Hoarseness or sore throat
⦿ Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
⦿ Sensation of a lump in throat
⦿ Hiccups
Patients with mild symptoms may not need any tests. However, in case of severe or repetitive symptoms, doctor prescribes following tests :
⦿ Upper endoscopy (EGD)
⦿ Ambulatory acid (pH) probe tests
⦿ Esophageal manometry
⦿ Stool occult blood test
⦿ An X-ray of upper digestive system
⦿ Upper endoscopy (EGD)
⦿ Ambulatory acid (pH) probe tests
⦿ Esophageal manometry
⦿ Stool occult blood test
⦿ An X-ray of upper digestive system
Most of the people can manage the GERD discomfort with dietary and lifestyle changes along with some over-the-counter medications like antacids, H2 receptor blockers or proton pump inhibitors. But some people with GERD may need stronger medications, or even surgery, to reduce the symptoms.
⦿ Surgery to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter (Nissen fundoplication)
⦿ Surgery to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter (Linx)
⦿ Surgery to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter (Nissen fundoplication)
⦿ Surgery to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter (Linx)
⦿ Laparoscopy is less invasive
⦿ Recovery time is shorter
⦿ Almost no scar
⦿ Less chances of infection
⦿ Recovery time is shorter
⦿ Almost no scar
⦿ Less chances of infection